 , with help from Nils Schlörer and others. Any additions (new papers, new nuclei) are welcome. This also serves as a shift prediction bibliography.
, with help from Nils Schlörer and others. Any additions (new papers, new nuclei) are welcome. This also serves as a shift prediction bibliography.This is an overview of errors achieved by various nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) shift prediction methods over time. This list is restricted to solution NMR of small organic molecules, e. g. protein or solid NMR prediction papers are not considered. Previous versions of this table were published in Prediction of chemical shift in NMR: a review and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Artificial Intelligence. The table and the image have been compiled by Stefan Kuhn  , with help from Nils Schlörer and others. Any additions (new papers, new nuclei) are welcome. This also serves as a shift prediction bibliography.
, with help from Nils Schlörer and others. Any additions (new papers, new nuclei) are welcome. This also serves as a shift prediction bibliography.
As explained in the papers, the figures need to be considered with care. In particular, the issue of training and test sets and their influence on the results needs to be considered. Also note:
The following table shows Historically achieved MAEs for various methods and datasets. It contains publications known to us by 21/9/2025.
| Date | 1H MAE (ppm) | 13C MAE (ppm) | 17O MAE (ppm) | 15N MAE (ppm) | 19F MAE (ppm) | 195Pt MAE (ppm) | Method | Training | Test Dataset | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1990 | - | 5.5** | - | - | - | - | Pretsch increments | C13Shift | CSEARCH | [1] |
| 4/1992 | - | 1.56 | - | - | - | - | Optimized Increments | OPSI | 3 organic molecules | [2] |
| 5/1994 | 0.19** | - | - | - | - | - | Pretsch increments | Custom | 200 molecules | [3] |
| 7/1997 | - | 1.217**** | - | - | - | - | Pyridine increments | - | disubst pyridines | [35] |
| 7/1997 | - | 2.42**** | - | - | - | - | Pyridine increments | - | trisubst pyridines | [35] |
| 7/1997 | - | 3.665**** | - | - | - | - | AROSIM with orthocorrection | - | disubst pyridines | [35] |
| 7/1997 | - | 2.951**** | - | - | - | - | AROSIM with orthocorrection | - | trisubst pyridines | [35] |
| 12/2000 | - | 2.4 | - | - | - | - | classic neural network | 57 sesquiterpene lactones | 11 organic molecules | [4] |
| 1/2002 | 0.25 | - | - | - | - | - | classic neural network | 120 organic molecules | 259 organic molecules | [5] |
| 8/2002 | - | 1.2 | - | - | - | - | classic neural network | SpecInfo | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 2.4 | - | - | - | - | classic neural network | SpecInfo | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 3.8 | - | - | - | - | Pretsch increments | ChemDraw Pro | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 3.7 | - | - | - | - | Pretsch increments | SpecTool | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 1.0 | - | - | - | - | HOSE | SpecInfo | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 2.7 | - | - | - | - | HOSE | PredictIt | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 1.7 | - | - | - | - | HOSE | CNMR 6.0 | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 3.4 | - | - | - | - | Cosmas 4.5 | n/a | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 4.0 | - | - | - | - | Gaussian 98 | n/a | Taxol | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 1.9 | - | - | - | - | classic neural network | SpecInfo | 1547 shifts/100 molecules | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 2.5 | - | - | - | - | classic neural network | SpecInfo | 1547 shifts/100 molecules | [6] |
| 8/2002 | - | 1.4 | - | - | - | - | SpecInfo | SpecInfo | 1547 shifts/100 molecules | [6] |
| 5/2007 | - | 1.59 | - | - | - | - | ACD/Labs predictor | ACD/Labs | NMRShiftDB | [7] |
| 5/2007 | - | 2.22 | - | - | - | - | CSEARCH | CSEARCH | NMRShiftDB | [7] |
| 1/2008 | 0.28 | - | - | - | - | - | CHARGE | n/a | Wiley 1H NMR database | [8] |
| 1/2008 | 0.30 | - | - | - | - | - | Pretsch Increments | n/a | Wiley 1H NMR database | [8] |
| 1/2008 | 0.18 | - | - | - | - | - | Pretsch 3D increments | n/a | Wiley 1H NMR database | [8] |
| 1/2008 | 0.28 | - | - | - | - | - | Combined | n/a | Wiley 1H NMR database | [8] |
| 1/2008 | 0.18 | 1.59 | - | - | - | - | NN | 13C 207,000, 1H 189,000 | 13C 118,000, 1H 116,000 compounds | [45] |
| 1/2008 | 0.18 | 1.71 | - | - | - | - | PLS | 13C 207,000, 1H 189,000 | 13C 118,000, 1H 116,000 compounds | [45] |
| 9/2008 | 0.154 | - | - | - | - | - | HOSE | NMRShiftDB | * | [9] |
| 9/2008 | 0.18 | - | - | - | - | - | J48 | NMRShiftDB | * | [9] |
| 9/2008 | 0.182 | - | - | - | - | - | RF | NMRShiftDB | * | [9] |
| 9/2008 | 0.215 | - | - | - | - | - | SVM | NMRShiftDB | * | [9] |
| 5/2009 | - | 1.85 | - | - | - | - | custom encoding partial least squares regression | 190,000 structures | 16,000 structures | [10] |
| 1/2010 | - | 1.58 | - | - | - | - | HOSE | ACD/Labs | 205 molecules/2531 shifts | [11] |
| 1/2010 | - | 1.91 | - | - | - | - | NN | ACD/Labs | 205 molecules/2531 shifts | [11] |
| 1/2010 | - | 2.15 | - | - | - | - | increment | n/a | 205 molecules/2531 shifts | [11] |
| 1/2010 | - | 3.29 | - | - | - | - | DFT-GIAO | n/a | 205 molecules/2531 shifts | [11] |
| 1/2010 | 0.1081 | - | - | - | - | - | improved HOSE | in house | 282 | [12] |
| 4/2019 | 0.25 | 2.82 | - | - | - | - | stereo HOSE | nmrshitdb2 | * | [13] |
| 4/2019 | 0.29 | 3.52 | - | - | - | - | HOSE | nmrshitdb2 | * | [13] |
| 5/2019 | - | 1.63 | - | - | - | - | modgraph (HOSE + NN) | modgraph | 13 molecules | [14] |
| 5/2019 | - | 2.2 | - | - | - | - | ML | MestreLab | 13 molecules | [14] |
| 5/2019 | - | 1.7 | - | - | - | - | ML | MestreLab | 13 molecules | [14] |
| 5/2019 | - | 1.3 | - | - | - | - | Ensemble of previous three | as per method | 13 molecules | [14] |
| 8/2019 | 0.28 | 1.43 | - | - | - | - | CNN | subset of nmrshitdb2 | * | [15] |
| 11/2019 | 0.23 | 2.45 | - | - | - | - | ML | DFT calculations | 410 structures | [16] |
| 4/2020 | 0.224 | 1.355 | - | - | - | - | MPNN | subset of nmrshitdb2 | * | [17] |
| 6/2020 | 0.18*** | 2.1*** | - | - | - | - | DFT+ML | 90% of 476 13C and 270 1H | 10% of 476 13C and 270 1H | [51] |
| 7/2020 | 0.243 | 1.552 | - | - | - | - | MPNN | subset of nmrshitdb2 | subset of nmrshitdb2 | [42] |
| 2/2021 | 0.11*** | 0.70*** | 1.69*** | 2.47*** | - | - | Δ-machine learning | 57456 DFT calculations | 3780 DFT calculations | [18] |
| 8/2021 | - | - | - | 6.12 | - | - | kernel ridge regression | DFT 623 molecule | DFT 205 molecules | [19] |
| 12/2021 | 0.10 | 1.26 | - | - | - | - | GNN | Subset of nmrshitdb2 | * | [32] |
| 3/2022 | 0.28 | 0.95 | - | - | - | - | DU8ML | 11 K experimental chemical shifts | ? | [47] |
| 5/2022 | 0.14 | 1.21 | - | - | - | - | ML-J-DP4 | 17,000 | 10,000 | [48] |
| 6/2022 | - | 1.0-1.5**** | - | - | - | - | DU8ML | 10,890 shift values | No systematic evaluation done | [46] |
| 8/2022 | - | - | - | - | 52.63 | - | CNN | 19F subset of nmrshitdb2 | * | [20] |
| 8/2022 | - | - | - | - | 8.88 | - | improved HOSE | 19F subset of nmrshitdb2 | * | [20] |
| 8/2022 | 0.191 | 1.228 | - | - | - | - | GNN | Subset of nmrshitdb2 | * | [31] |
| 2/2023 | - | - | - | - | - | 170.07 | Laplacian kernel ridge regression | Own | * | [34] |
| 9/2023 | 0.209 | 2.18 | - | - | - | - | FullSSPrUCe (GNN) | nmrshiftdb2 | * | [21] |
| 11/2023 | 0.168 | 2.938 | - | - | - | - | ComENet | GlycoNMR 80% | GlycoNMR 10% | [22] |
| 11/2023 | 0.145 | 2.550 | - | - | - | - | DimeNet++ | GlycoNMR 80% | GlycoNMR 10% | [22] |
| 11/2023 | 0.140 | 2.492 | - | - | - | - | SchNet | GlycoNMR 80% | GlycoNMR 10% | [22] |
| 11/2023 | 0.146 | 3.044 | - | - | - | - | SphereNet | GlycoNMR 80% | GlycoNMR 10% | [22] |
| 12/2023 | 0.138 | 1.79 | - | - | - | - | fragment-based | COLMAR | 768 COLMAR Metabolites | [23] |
| 3/2024 | 0.210 | 2.228 | - | - | - | - | GNN | nmrshiftdb2 subset | HMDB and CH-NMR-NP | [24] |
| 5/2024 | 0.10 | - | - | - | - | - | GNN | PROSPRE 3755 compounds | PROSPRE 272 compounds | [25] |
| 5/2024 | - | 0.7 | - | - | - | - | DFT | - | 132 shifts | [26] |
| 6/2024 | 0.185 | 0.944 | - | - | - | - | DFT+3D GNN | nmrshiftdb2 80% | nmrshiftdb2 20% | [27] |
| 6/2024 | - | - | - | - | 3.636 | - | Graph convolutional network | 1900 fluorinated compounds | 100 fluorinated compounds | [50] |
| 7/2024 | - | 0.5**** | - | - | - | - | GNN | 1637 benzenic compounds | 114 benzenic structures | [43] |
| 8/2024 | 0.10 | 2.0 | 6.4 | 2.1 | - | - | ML with QM-based features | ANI-1 with DFT | 40 molecules | [49] |
| 8/2024 | 0.035**** | 0.31**** | - | - | - | - | E(3) equivariant graph neural network | CASPER | Monosaccharides | [29] |
| 8/2024 | 0.026**** | 0.23**** | - | - | - | - | E(3) equivariant graph neural network | CASPER | Disaccharides | [29] |
| 8/2024 | 0.033**** | 0.30**** | - | - | - | - | E(3) equivariant graph neural network | CASPER | Trisaccharides | [29] |
| 9/2024 | - | 1.28 | - | - | - | - | transfer learning with GNNs | nmrshiftdb2 subset | nmrshiftdb2 subset | [39] |
| 11/2024 | 0.158 | 1.189 | - | - | - | - | GNN | nmrshiftdb2 | * | [30] |
| 12/2024 | - | - | - | - | 3.31 | - | Gradient Boosting Regression | - | 501 fluorinated compounds | [33] |
| 2/2025 | 0.167 | 2.025 | - | - | - | - | Multi-task pre-training and unsupervised learning | nmrshiftdb2 | 479 molecules | [36] |
| 3/2025 | 0.07 | 0.76 | - | 2.26 | - | - | IMPRESSION 2 | IG2, DFT generated | internal | [40] |
| 4/2025 | 0.020 | 0.262 | - | - | - | - | SE(3) Transformer with pre-training and fine-tuning (NMRNet) | 4.8 million structures | ? | [44] |
| 7/2025 | - | 0.73 | - | - | - | - | polarizable atom interaction neural network (PAiNN) | 17,588 molecules from Exp22K | 2,200 molecules from Exp22K | [38] |
| 8/2025 | 0.05*** | 0.76*** | - | - | - | - | SpookyNet, transformer network with self-attention | ≈2.7 million equilibrium geometry and chemical shift calculations for a diverse collection of organic molecules | 601 marine natural products | [41] |
| 8/2025 | 0.09*** | 1.02*** | - | - | - | - | SpookyNet, transformer network with self-attention | ≈2.7 million equilibrium geometry and chemical shift calculations for a diverse collection of organic molecules | 601 marine natural products, with equilibrium geometries reproducing those in the training set | [41] |
| 1/2026 | 0.1709 | 0.9270 | - | - | - | - | permutation-invariant set supervision problem with NMRNet | nmrshiftdb2 | 4:1 random split | [52] |
| 1/2026 | 0.0559 | 0.5060 | - | - | - | - | permutation-invariant set supervision problem with NMRNet | millions of molecular-spectral entries from the literature and nmrshiftdb2 | 4:1 random split | [52] |
This figure uses the data from the above table, showing results for 1H and 13C NMR predictions from 1990 until now, ordered by publication time. The light lines give the least squares linear regression up to 6/2024 (this is the data from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Artificial Intelligence). The dashed light lines are the least squares linear regression for data up to 2/2001 (this is the data from Prediction of chemical shift in NMR: a review). Data from those timespans, which have been added later and are not in the respective publications, are not included in the regression. Squares indicate ab initio calculations, triangles deep learning methods, pentagons combined methods. As before, conclusions require careful analysis.
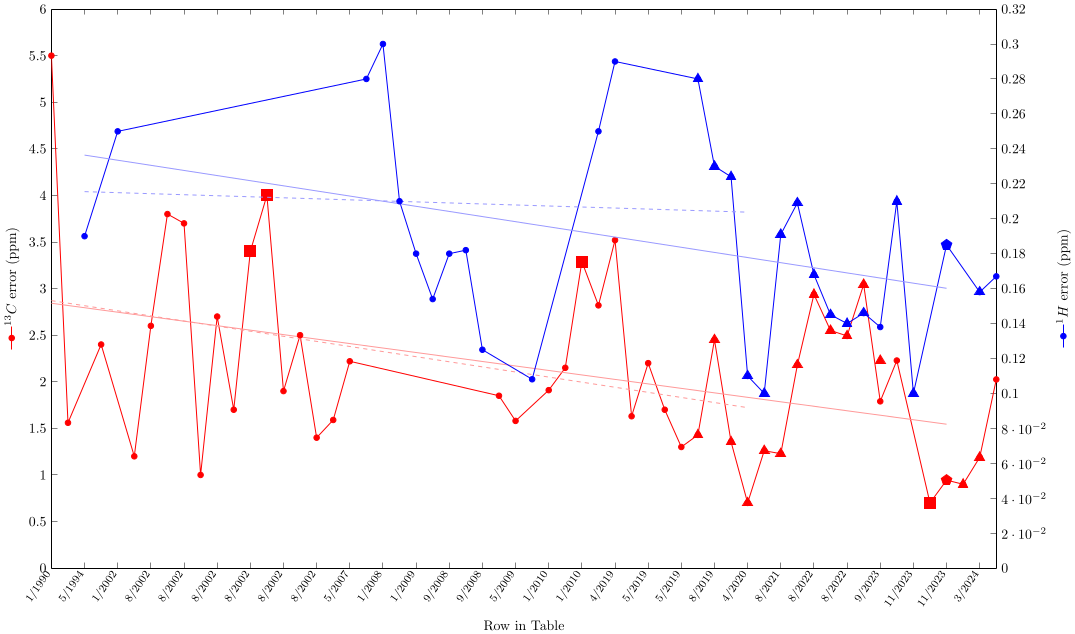
Chart as pdf
Here follows a list of reviews about either spectrum prediction in particular or about NMR and AI/ML in general: